Vaccine developed against Ebola
- Published
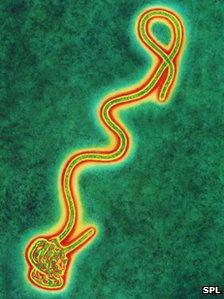
Scientists have developed a vaccine that protects mice against a deadly form of the Ebola virus.
First identified in 1976, Ebola fever kills a majority of the people it infects.
The researchers say that this is the first Ebola vaccine to remain viable long-term and can therefore be successfully stockpiled.
The results are reported in the journal Proceedings of National Academy of Sciences.
Ebola is transmitted via bodily fluids, and can become airborne. Sufferers experience nausea, vomiting, internal bleeding and organ failure before they die.
Although few people contract Ebola each year, its effects are so swift and devastating that it is often feared that it could be used against humans in an act of terroism.
All previously developed vaccines have relied on injecting intact, but crippled, viral particles into the body.
Long-term storage tends to damage the virus, paralysing the vaccine's effectiveness.
The new vaccine contains a synthetic viral protein, which prompts the immune system to better recognise the Ebola virus, and is much more stable when stored long-term.
The vaccine protects 80% of the mice injected with the deadly strain, and survives being "dried down and frozen," said biotechnologist Charles Arntzen from Arizona State University who was involved in its development.
He said the next step is to try the vaccine on a strain of Ebola that is closer to the one that infects humans.
- Published10 July 2009
- Published22 August 2010
- Published22 January 2008